+86-18186629601
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH CAS 143413-47-2 Product Information
| CAS No | 143413-47-2 |
| Product Name | H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH |
| Synonyms | H-RRRRRRRRR-NH2; RRRRRRRRR; (ARG)9; H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH; Nonaarginine; H(-Arg)9-OH, Nonaarginine; (Arg)9 peptide; Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg |
| Free Sample | Available |
| Molecular Formula | C54H110N36O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 1423.69 |
| Purity | 99% |
| Free Shipping | YES |
H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH CAS 143413-47-2 Product Information
| CAS No | 143413-47-2 |
| Product Name | H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH |
| Synonyms | H-RRRRRRRRR-NH2; RRRRRRRRR; (ARG)9; H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH; Nonaarginine; H(-Arg)9-OH, Nonaarginine; (Arg)9 peptide; Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg |
| Free Sample | Available |
| Molecular Formula | C54H110N36O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 1423.69 |
| Purity | 99% |
| Free Shipping | YES |
H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH CAS 143413-47-2 Chemical Properties
| Density | VJKXESGORYEAGC-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
| Solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Storage conditions | Store at -20°C |
| Form | powdered solid |
| Source | Artificial chemical synthesis is limited to scientific research use and may not be used on the human body. |
| Salt system | Optional TFA, HAc, HCl or others |
H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH CAS 143413-47-2 Chemical Properties
| Density | VJKXESGORYEAGC-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
| Solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Storage conditions | Store at -20°C |
| Form | powdered solid |
| Source | Artificial chemical synthesis is limited to scientific research use and may not be used on the human body. |
| Salt system | Optional TFA, HAc, HCl or others |
H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH CAS 143413-47-2 Uses And Synthesis Methods
Definition
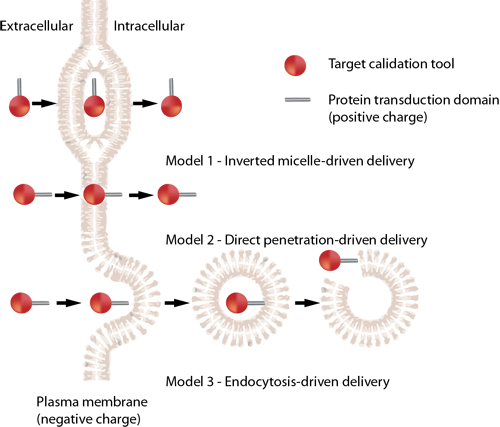
(Arg)9 (Nona-L-arginine; Peptide R9) is a cell-permeable peptide with an IC50 value of 0.78 μM for neuroprotection in the glutamate experimental model. Cell permeable peptides (CPPs) are carriers with small peptide domains that can freely cross cell membranes. They are mainly used as carriers of proteins and nucleic acids into the cell1.
Target
IC50: 0.78 μM (neuroprotection)
Structural Characteristics
CPPs typically have an amino acid composition containing either a high relative abundance of positively charged, cationic amino acids such as lysine or arginine, or have sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids3. Some examples include: TAT peptide-YGRKKRRQRRR, lipid membrane translocating peptide-KKAAAVLLPVLLAAP and Antennapedia leader peptide-KKWKMRRNQFWVKVQRG.
Mode of action
CPPs enter the cell with their carrier by either of three mechanisms: Direct delivery that involves energy independent entry of the CPPs in to the cell4, endocytosis where the cells take up the CPPs by imbibing them with their cell membranes5 and translocation through the formation of transient structures which is yet to be understood6.
Functions
CPPs have found numerous applications in medicine as drug delivery agents in the treatment of different diseases including cancer, virus inhibitors, contrast agents for cell labeling a classical example is Green Fluorescent protein GFP, as MRI contrast agents, quantum dots7. TAT is very effective in delivering drugs in vitro and in vivo and so far a peptide that matches its efficiency has not been found7.
H-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-ARG-OH CAS 143413-47-2 Uses And Synthesis Methods
Definition
(Arg)9 (Nona-L-arginine; Peptide R9) is a cell-permeable peptide with an IC50 value of 0.78 μM for neuroprotection in the glutamate experimental model. Cell permeable peptides (CPPs) are carriers with small peptide domains that can freely cross cell membranes. They are mainly used as carriers of proteins and nucleic acids into the cell1.

Target
IC50: 0.78 μM (neuroprotection)
Structural Characteristics
CPPs typically have an amino acid composition containing either a high relative abundance of positively charged, cationic amino acids such as lysine or arginine, or have sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids3. Some examples include: TAT peptide-YGRKKRRQRRR, lipid membrane translocating peptide-KKAAAVLLPVLLAAP and Antennapedia leader peptide-KKWKMRRNQFWVKVQRG.
Mode of action
CPPs enter the cell with their carrier by either of three mechanisms: Direct delivery that involves energy independent entry of the CPPs in to the cell4, endocytosis where the cells take up the CPPs by imbibing them with their cell membranes5 and translocation through the formation of transient structures which is yet to be understood6.
Functions
CPPs have found numerous applications in medicine as drug delivery agents in the treatment of different diseases including cancer, virus inhibitors, contrast agents for cell labeling a classical example is Green Fluorescent protein GFP, as MRI contrast agents, quantum dots7. TAT is very effective in delivering drugs in vitro and in vivo and so far a peptide that matches its efficiency has not been found7.