+86-18186629601
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Cell Adhesive Peptide CAS 109292-46-8 Product Information
| CAS No | 109292-46-8 |
| Product Name | Cell Adhesive Peptide |
| Synonyms | RGDC; ARG-GLY-ASP-CYS; H-ARG-GLY-ASP-CYS-OH; Arg-Gly-Asp-Cys|RGDC; REFDUPL:H-Arg-Gly-Asp-Cys-OH; L-Cysteine,L-arginylglycyl-L-α-aspartyl-; (3S)-3-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-4-[[(1R)-1-carboxy-2-sulfanylethyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoicacid |
| Free Sample | Available |
| Molecular Formula | C15H27N7O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 449.48 |
| Purity | 99% |
| Free Shipping | YES |
Cell Adhesive Peptide CAS 109292-46-8 Product Information
| CAS No | 109292-46-8 |
| Product Name | Cell Adhesive Peptide |
| Synonyms | RGDC; ARG-GLY-ASP-CYS; H-ARG-GLY-ASP-CYS-OH; Arg-Gly-Asp-Cys|RGDC; REFDUPL:H-Arg-Gly-Asp-Cys-OH; L-Cysteine,L-arginylglycyl-L-α-aspartyl-; (3S)-3-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-4-[[(1R)-1-carboxy-2-sulfanylethyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoicacid |
| Free Sample | Available |
| Molecular Formula | C15H27N7O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 449.48 |
| Purity | 99% |
| Free Shipping | YES |
Cell Adhesive Peptide CAS 109292-46-8 Chemical Properties
| Density | 1?+-.0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Storage conditions | -15°C |
| Acidity coefficient (pKa) | 2.81±0.10(Predicted) |
| Color | white |
| Form | powdered solid |
| Source | Artificial chemical synthesis is limited to scientific research use and may not be used on the human body. |
| Salt system | Optional TFA, HAc, HCl or others |
Cell Adhesive Peptide CAS 109292-46-8 Chemical Properties
| Density | 1?+-.0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Storage conditions | -15°C |
| Acidity coefficient (pKa) | 2.81±0.10(Predicted) |
| Color | white |
| Form | powdered solid |
| Source | Artificial chemical synthesis is limited to scientific research use and may not be used on the human body. |
| Salt system | Optional TFA, HAc, HCl or others |
Cell Adhesive Peptide CAS 109292-46-8 properties, Uses and Production Process
Biological activity
Arg-Gly-Asp-Cys is the binding motif between fibronectin and cell adhesion molecules and can inhibit platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding.
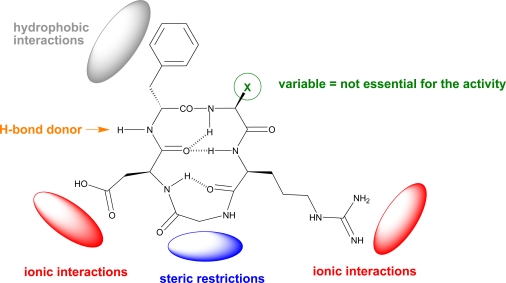
Discovery
Synthetic cell adhesion peptides were first derived from laminin. The peptide PA22-2 (CSRARKQAASIKVAVSADR-NH2) derived from laminin was found to function as a cell adhesion molecule which was tested with mouse mast cells1.
Classification
Cell adhesion peptides for the most part are extracellular matrix proteins1.
Structural Characteristics
Numerous cell adhesion peptides have been synthesized to date. Some examples include: RU-1 (LNIVSVNGRHX), RX-1 (DNRIRLQAKXX), GD-1 (KATPMLKMRTSFHGCIK), GD-2 (KEGYKVRLDLNITLEFRTTSK), GD-3 (KNLEISRSTFDLLRNSYGVRK), GD-6 (KQNCLSSRASFRGCVRNLRLSR), HGD-6 (KQKCLRSQTSFRGCLRKLALIK), SGD-6 (CRNRGRCNSSLFQVRSRKLLSA), HSGD-6 (KQCLKSQRSFTRGLCRLKAKIL), AG-1 (KLLISRARKQÁASIK), F17 (LERKYENDQKYLEDKA) and KRGD (VEKRGDREEA). Peptides that are linear and cyclic in nature have been synthesized2.
Mode of action
Cell adhesion peptides can bind to the cell membrane and trigger adhesion of cells3.
Functions
Cell adhesion peptides have known to increase signaling via receptors3. They have been shown to decrease tumor metastasis and growth in experimental animals3. These peptides also induce Ca2+ signaling and modulate platelet activity3.
Cell Adhesive Peptide CAS 109292-46-8 properties, Uses and Production Process
Biological activity
Arg-Gly-Asp-Cys is the binding motif between fibronectin and cell adhesion molecules and can inhibit platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding.

Discovery
Synthetic cell adhesion peptides were first derived from laminin. The peptide PA22-2 (CSRARKQAASIKVAVSADR-NH2) derived from laminin was found to function as a cell adhesion molecule which was tested with mouse mast cells1.
Classification
Cell adhesion peptides for the most part are extracellular matrix proteins1.
Structural Characteristics
Numerous cell adhesion peptides have been synthesized to date. Some examples include: RU-1 (LNIVSVNGRHX), RX-1 (DNRIRLQAKXX), GD-1 (KATPMLKMRTSFHGCIK), GD-2 (KEGYKVRLDLNITLEFRTTSK), GD-3 (KNLEISRSTFDLLRNSYGVRK), GD-6 (KQNCLSSRASFRGCVRNLRLSR), HGD-6 (KQKCLRSQTSFRGCLRKLALIK), SGD-6 (CRNRGRCNSSLFQVRSRKLLSA), HSGD-6 (KQCLKSQRSFTRGLCRLKAKIL), AG-1 (KLLISRARKQÁASIK), F17 (LERKYENDQKYLEDKA) and KRGD (VEKRGDREEA). Peptides that are linear and cyclic in nature have been synthesized2.
Mode of action
Cell adhesion peptides can bind to the cell membrane and trigger adhesion of cells3.
Functions
Cell adhesion peptides have known to increase signaling via receptors3. They have been shown to decrease tumor metastasis and growth in experimental animals3. These peptides also induce Ca2+ signaling and modulate platelet activity3.