+86-18186629601
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Amyloid β-Protein (1-40) CAS 131438-79-4 Product Information
| CAS No | 131438-79-4 |
| Product Name | AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 1-40) TRIFLUOROACETATE |
| Synonyms | AMYLOIDB-PROTEINFRAGMENT1-40; Amyloidb-Peptide(1-40)(human); H-Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Gly-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Phe-Glu-Val-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Phe-Glu-Val-Arg-His-Gln-Lys-Leu-Val-Gly-Phe-Phe-Ala-Glu-Asp-Val-Gly-Ser-Asn-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ile-Ile-Gly-Leu-Met-Val-Gly-Gly-Val-Val-OH; AmyloidbetaProteinfragment1-40HClSalt; amyloidβproteinfragment1-40; aβ40; SS-AMYLOID(1-40),RAT; M.W.4329.86C194H295N53O58S |
| Free Sample | Available |
| Molecular Formula | C194H295N53O58S |
| Molecular Weight | 4329.8034 |
| Purity | 99% |
| Free Shipping | YES |
Amyloid β-Protein (1-40) CAS 131438-79-4 Product Information
| CAS No | 131438-79-4 |
| Product Name | AMYLOID BETA-PROTEIN (HUMAN, 1-40) TRIFLUOROACETATE |
| Synonyms | AMYLOIDB-PROTEINFRAGMENT1-40; Amyloidb-Peptide(1-40)(human); H-Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Gly-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Phe-Glu-Val-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Phe-Glu-Val-Arg-His-Gln-Lys-Leu-Val-Gly-Phe-Phe-Ala-Glu-Asp-Val-Gly-Ser-Asn-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ile-Ile-Gly-Leu-Met-Val-Gly-Gly-Val-Val-OH; AmyloidbetaProteinfragment1-40HClSalt; amyloidβproteinfragment1-40; aβ40; SS-AMYLOID(1-40),RAT; M.W.4329.86C194H295N53O58S |
| Free Sample | Available |
| Molecular Formula | C194H295N53O58S |
| Molecular Weight | 4329.8034 |
| Purity | 99% |
| Free Shipping | YES |
CYCLO(-GLY-PHE) CAS 10125-07-2 Chemical Properties
| Storage conditions | -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O: 6#160;mg/mL |
| Water solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water |
| Color | white |
| Form | powder |
| Source | Artificial chemical synthesis is limited to scientific research use and may not be used on the human body. |
| Salt system | Optional TFA, HAc, HCl or others |
| Generation cycle | 2-3 weeks |
CYCLO(-GLY-PHE) CAS 10125-07-2 Chemical Properties
| Storage conditions | -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O: 6#160;mg/mL |
| Water solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water |
| Color | white |
| Form | powder |
| Source | Artificial chemical synthesis is limited to scientific research use and may not be used on the human body. |
| Salt system | Optional TFA, HAc, HCl or others |
| Generation cycle | 2-3 weeks |
CYCLO(-GLY-PHE) CAS 10125-07-2 Uses And Synthesis Methods
Biological activity
β-Amyloid (1-40) TFA is a primary protein in plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease
Amyloid Peptide Background
Amyloid beta (Aβ or Abeta) is a 36–43 amino acid peptide processed from amyloid precursor protein. Aβ is a component of the amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer's disease. Evidence has shown that Aβ is a multifunctional peptide with significant non-pathological activities. Aβ is a major component of the deposits found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. In the brains of patients with sporadic Alzheimer's disease, Aβ levels are elevated, causing cerebrovascular lesions and neurotoxicity. Aβ protein is produced by the sequential action of β and γ secretases. γ-secretase produces the C-terminus of the Aβ peptide and cleaves it at the transmembrane domain of APP, which can produce many isomers with a length of 36-43 amino acid residues.The most common isomers are Aβ40 and Aβ42. The longer form of Aβ is produced by cleavage in the endoplasmic reticulum, while the shorter form of Aβ is produced in the trans-Golgi reticulum.
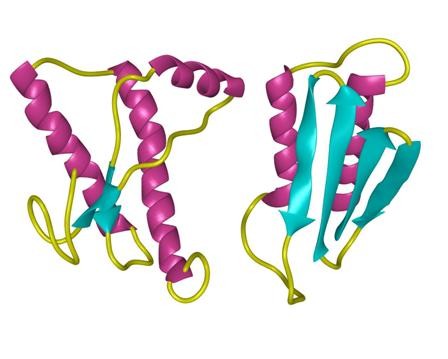
structure of Amyloid β-Peptide (1-40) (human)
In vitro studies
β-Amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) are major components of senile plaque amyloids, are physiological peptides present in the brain, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma. The levels of CSF β-Amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) show a U-shaped natural course in normal aging.Chronic infusion of beta-amyloid (1-40) for 14 days into the rat cerebroventricle decreased the activity of soluble protein kinase C (PKC) in the hippocampus. Subcellular translocation of PKC to membrane fraction in hippocampal slices of rats treated with beta-amyloid (1-40) is completely abolished under acute stimulation with 0.5 microM phorbol-dibutyrate (PDBu). The further aggregation of β-Amyloid (1-40)
1. Solid Aβ peptide was dissolved in cold hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP). The peptide was incubated at room temperature for at least 1h to establish monomerization and randomization of structure.
2. The HFIP was removed by evaporation, and the resulting peptide was stored as a film at -20 or -80°C.
3. The resulting film was dissolved in anhydrous DMSO at 5 mM and then diluted into the appropriate concentration and buffer (serum- and phenol red-free culture medium) with vortexing.
4. Next, the solution was age 48h at 4-8°C. The sample was then centrifuged at 14000g for 10 min at 4-8°C; the soluble oligomers were in the supernatant.The supernatant was diluted 10-200-fold for experiments. Methods vary depends on the downstream applications.
In vivo studies
Chronic infusion of β-Amyloid (1-40) into rat cerebroventricle leads to deficit in spatial and non-spatial memory formation.Chronic treatment of β-Amyloid (1-40) does not change lever-pressing performance significantly, but performance declined significantly 30 days after termination of the chronic daily regimen. The soluble unaggregated form of β-Amyloid (1-40), injected into the dorsal hippocampus, does not appear to have behavioral effects on performance or short-term working memory in rats, but multiple repeat injections produced performance decrements several weeks later. Repeated injection of β-Amyloid (1-40) through indwelling cannulae shows promise for development of an animal model of Alzheimer's disease.
CYCLO(-GLY-PHE) CAS 10125-07-2 Uses And Synthesis Methods
Biological activity
β-Amyloid (1-40) TFA is a primary protein in plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease
Amyloid Peptide Background
Amyloid beta (Aβ or Abeta) is a 36–43 amino acid peptide processed from amyloid precursor protein. Aβ is a component of the amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer's disease. Evidence has shown that Aβ is a multifunctional peptide with significant non-pathological activities. Aβ is a major component of the deposits found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. In the brains of patients with sporadic Alzheimer's disease, Aβ levels are elevated, causing cerebrovascular lesions and neurotoxicity. Aβ protein is produced by the sequential action of β and γ secretases. γ-secretase produces the C-terminus of the Aβ peptide and cleaves it at the transmembrane domain of APP, which can produce many isomers with a length of 36-43 amino acid residues.The most common isomers are Aβ40 and Aβ42. The longer form of Aβ is produced by cleavage in the endoplasmic reticulum, while the shorter form of Aβ is produced in the trans-Golgi reticulum.

structure of Amyloid β-Peptide (1-40) (human)
In vitro studies
β-Amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) are major components of senile plaque amyloids, are physiological peptides present in the brain, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma. The levels of CSF β-Amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) show a U-shaped natural course in normal aging.Chronic infusion of beta-amyloid (1-40) for 14 days into the rat cerebroventricle decreased the activity of soluble protein kinase C (PKC) in the hippocampus. Subcellular translocation of PKC to membrane fraction in hippocampal slices of rats treated with beta-amyloid (1-40) is completely abolished under acute stimulation with 0.5 microM phorbol-dibutyrate (PDBu). The further aggregation of β-Amyloid (1-40)
1. Solid Aβ peptide was dissolved in cold hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP). The peptide was incubated at room temperature for at least 1h to establish monomerization and randomization of structure.
2. The HFIP was removed by evaporation, and the resulting peptide was stored as a film at -20 or -80°C.
3. The resulting film was dissolved in anhydrous DMSO at 5 mM and then diluted into the appropriate concentration and buffer (serum- and phenol red-free culture medium) with vortexing.
4. Next, the solution was age 48h at 4-8°C. The sample was then centrifuged at 14000g for 10 min at 4-8°C; the soluble oligomers were in the supernatant.The supernatant was diluted 10-200-fold for experiments. Methods vary depends on the downstream applications.
In vivo studies
Chronic infusion of β-Amyloid (1-40) into rat cerebroventricle leads to deficit in spatial and non-spatial memory formation.Chronic treatment of β-Amyloid (1-40) does not change lever-pressing performance significantly, but performance declined significantly 30 days after termination of the chronic daily regimen. The soluble unaggregated form of β-Amyloid (1-40), injected into the dorsal hippocampus, does not appear to have behavioral effects on performance or short-term working memory in rats, but multiple repeat injections produced performance decrements several weeks later. Repeated injection of β-Amyloid (1-40) through indwelling cannulae shows promise for development of an animal model of Alzheimer's disease.